Planet Nine: The Mystery of Our Solar System’s Hidden Giant 2025
Table of Contents
Introduction: The Enigma Beyond Neptune
For centuries, our understanding of the solar system has been shaped by the known planets orbiting our Sun. However, recent astronomical observations and studies suggest the existence of an elusive ninth planet, often referred to as “Planet Nine.” This hypothetical planet, residing far beyond Neptune, could potentially reshape our comprehension of the solar system’s structure and dynamics.
Historical Background: From Pluto to Planet Nine
The Demotion of Pluto
In 2006, the International Astronomical Union reclassified Pluto as a “dwarf planet,” reducing the number of recognized planets in our solar system to eight. This decision was based on criteria that Pluto did not meet, such as clearing its orbital path of other debris.
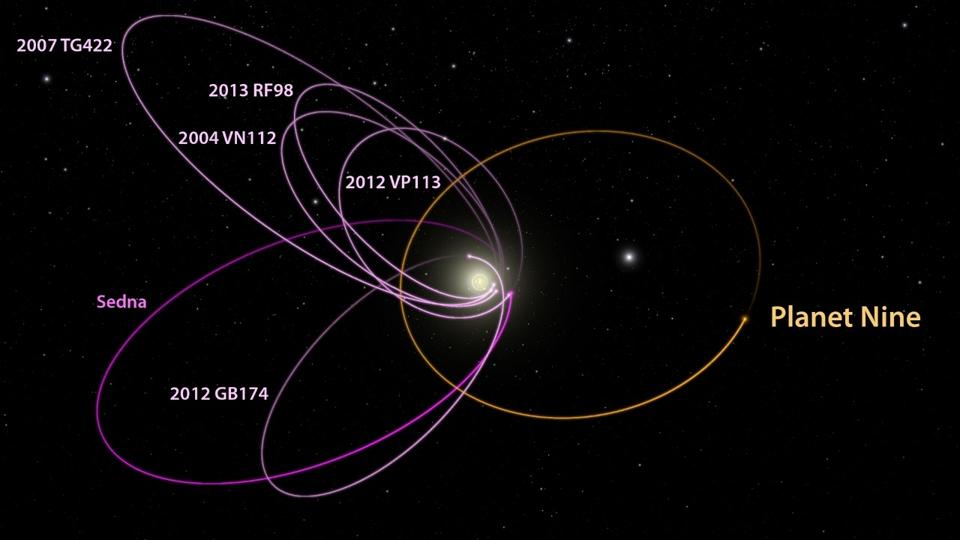
The Emergence of the Planet Nine Hypothesis
The concept of a ninth planet isn’t new; astronomers have long speculated about undiscovered celestial bodies influencing the orbits of known planets. However, the modern Planet Nine hypothesis gained traction in 2016 when Caltech researchers Mike Brown and Konstantin Batygin proposed the existence of a massive, distant planet to explain the peculiar clustering of certain trans-Neptunian objects (TNOs)
Recent Discoveries and Evidence (2025)
Discovery of 2017 OF201
In 2025, astronomers identified a new dwarf planet, designated 2017 OF201, situated far beyond Neptune’s orbit. This celestial body follows an extremely elongated orbit, taking approximately 25,000 years to complete one revolution around the Sun. While its discovery is significant, 2017 OF201 does not align with the gravitational patterns theorized by the proposed Planet Nine, potentially challenging its existence .Live Science
Infrared Observations
A recent study analyzed data from the Infrared Astronomical Satellite (IRAS) and Japan’s AKARI mission, identifying a potential candidate for Planet Nine. This object appears as a slowly moving infrared dot across images taken 23 years apart, consistent with characteristics expected of Planet Nine. However, further observations are necessary to confirm its identity .
Characteristics of the Hypothetical Planet Nine
Estimated Size and Mass
Planet Nine is hypothesized to be a super-Earth, with an estimated mass about 5 to 10 times that of Earth. Its diameter could be two to four times that of Earth, making it significantly larger than Pluto
Orbital Parameters
The planet is believed to orbit the Sun at a distance ranging from 400 to 800 astronomical units (AU), with a highly elongated and inclined orbit. It would take between 10,000 and 20,000 years to complete one full orbit .
Comparison with Known Planets
Unlike the eight known planets, which have relatively circular and coplanar orbits, Planet Nine’s orbit is expected to be highly eccentric and inclined, distinguishing it from its planetary counterparts.

Challenges in Detection
Technical Limitations
Detecting Planet Nine is challenging due to its vast distance from the Sun, making it extremely faint and difficult to observe with current telescopes. Its slow movement across the sky further complicates detection efforts .
Observational Biases
The limited number of observed TNOs and the vastness of the sky introduce observational biases, potentially affecting the perceived clustering of orbits and the inferred existence of Planet Nine .
Potential for Misidentification
Some objects initially considered as potential candidates for Planet Nine have been found to have orbital characteristics inconsistent with the hypothesis, highlighting the importance of thorough analysis and confirmation .

Implications of the Discovery
Revisions to Solar System Models
The confirmation of Planet Nine would necessitate significant revisions to existing models of the solar system, particularly concerning the formation and evolution of distant celestial bodies.
Insights into Planetary Formation
Understanding Planet Nine’s characteristics and origin could provide valuable insights into planetary formation processes, including the migration and scattering of planets in the early solar system.
Influence on Future Research
The pursuit of Planet Nine has already spurred advancements in observational techniques and data analysis methods, influencing future astronomical research and exploration endeavors.
Future Prospects
Upcoming Observational Missions
The Vera C. Rubin Observatory, set to commence operations soon, is expected to play a crucial role in the search for Planet Nine, offering enhanced capabilities for detecting faint, distant objects .
Collaborative Efforts
International collaborations and data-sharing initiatives among astronomers and institutions are vital for pooling resources and expertise in the ongoing quest to confirm or refute the existence of Planet Nine.
Role of Citizen Science
Citizen science projects, where amateur astronomers contribute to data analysis and observations, can augment professional efforts, potentially accelerating the discovery process.
Conclusion: The Ongoing Quest
The hypothesis of Planet Nine presents an intriguing possibility that challenges our current understanding of the solar system. While direct evidence remains elusive, ongoing research and technological advancements continue to bring us closer to uncovering the truth. The pursuit of this hidden giant not only fuels scientific curiosity but also exemplifies the dynamic and ever-evolving nature of astronomical exploration.
Read More – NexGL










